What's New in Swift 5.7 - WWDC2022
#iOS App Development, #Swift
Community update
Workgroups
Additionally to "Swift on Server" and "Diversity in Swift" work groups, "Swift Website", and "C++ Interoperability" workgroups were introduced
Mentorship program
The mentorship program was enhanced in the following areas:

Year-round availability for starter bug contributions for those who don't have a lot of free time (means have a job).
Here is the link to apply or check the details. You can find more info about the diversity initiative here.
Swift packages
New native toolchain installers that support RPMs for:
- Amazon Linux 2
- CentOS 7
RPMs can now be downloaded directly for swift.org. However, the toolchains are still experimental. So be careful.
Performance improvements
The long-term goal is to make Swift scalable and suitable for different areas of tasks, from high-level scripts and apps to bare metal applications.
To make the standard library smaller, they've replaced dependency on 3rd party Unicode library with fast native implementation.
No doubt that fast and small statically linked binaries are great. Statically linked standard library on Linux should make it more suitable for server containerized deployments.
As stated, the size reduction now allows apple to use Swift code even in their Secure Enclave Processor.
TOFU
TOFU which stands for Trust On First Use is a security protocol that fingerprints packages on the first download and ensures that afterward nothing is taken over.
Command plugins
Command plugins are a new way to improve tooling for developers.
- Generate documentation
- Reformat source code
- Generate test reports
Now, instead of having to use shell scripts, Swift can be used and it's also available for SPM packages which should make a good kick-off for open-source.
DocC Plugin
DocC is a tool to integrate documentation into the source code. Now it's also supported for Obj-C and C.
Here is an example of what a plugin that runs DocC may look like:
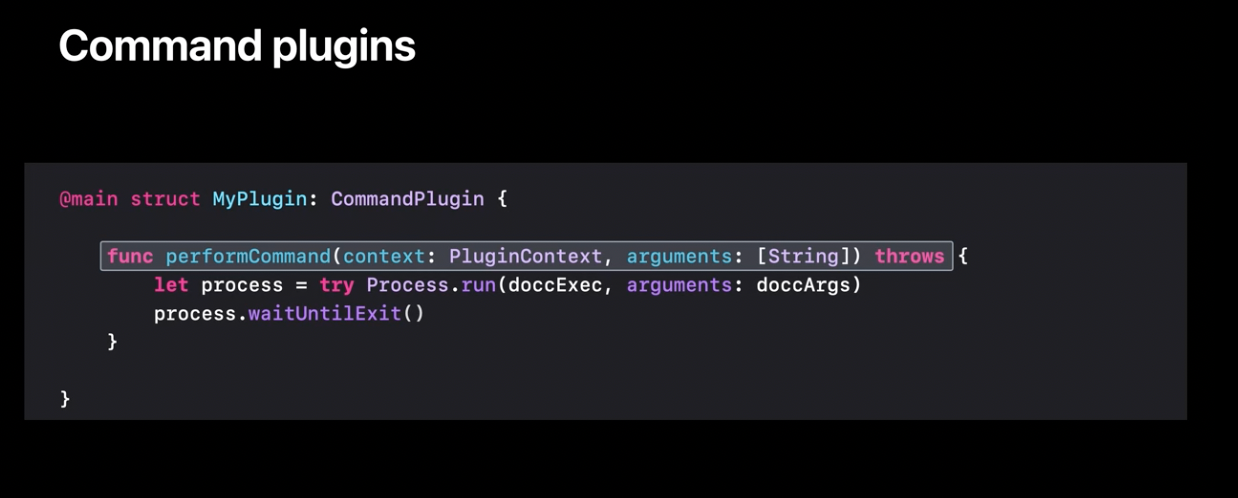
It can be run via SPM CLI or Xcode
Build tool plugins
Plugins allow developers to integrate additional steps during the build. Just like build phase scripts but also for packages.
Such as:
- Source code generation
- Resource processing
Plugins can be a part of the package:

Plugins are treated as swift executables that may have args inputs and result outputs.
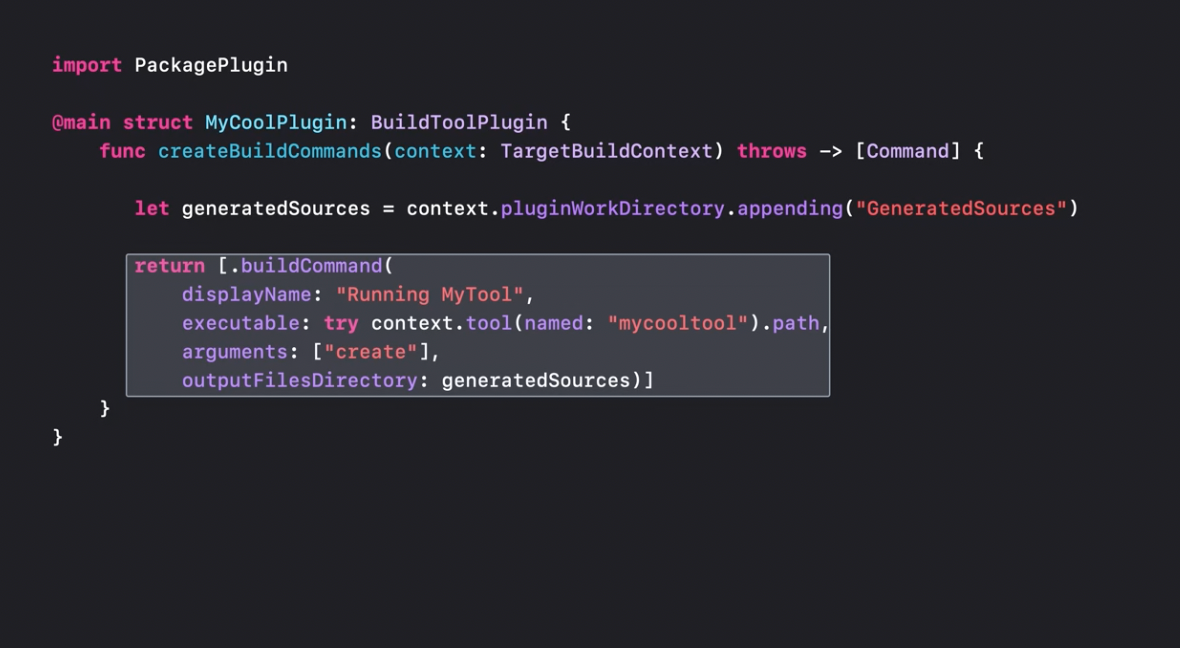
Recommended to watch:
- [[Meet swift Package plugins - WWDC2022]]
- [[Create Swift Package plugins - WWDC2022]]
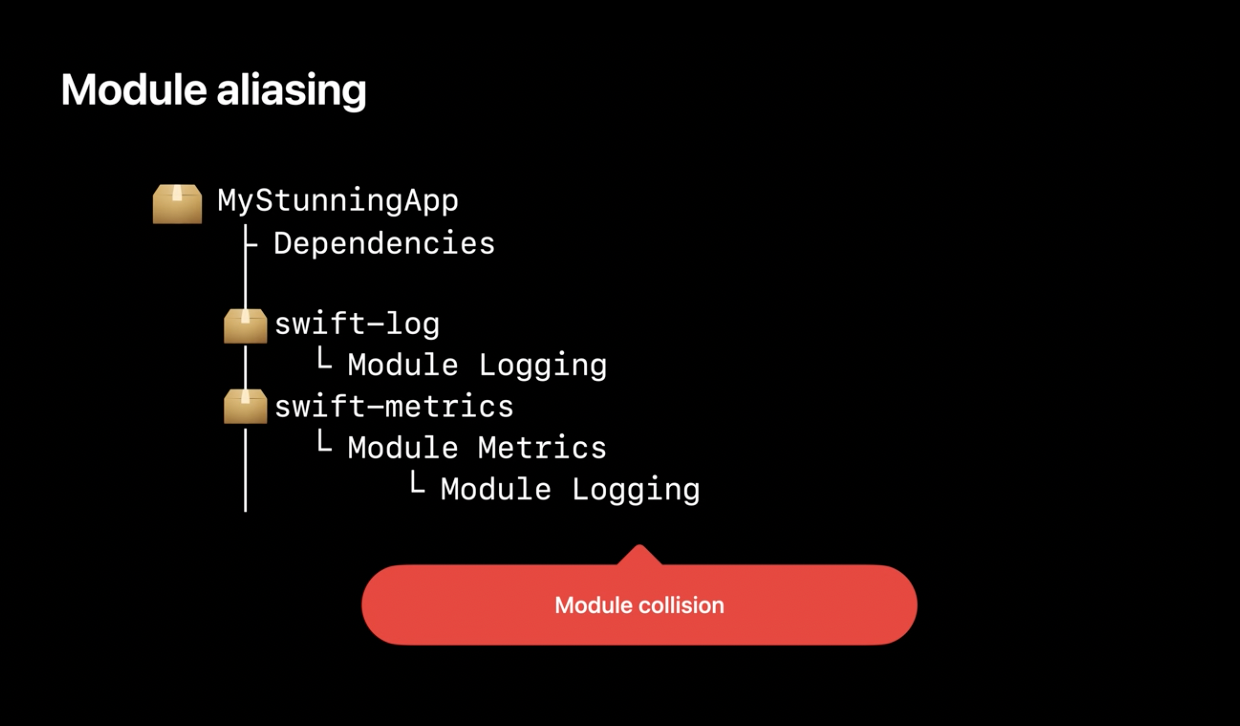
Module aliases
To avoid naming collisions between packages, modules aliases were introduced in SPM for Swift 5.7:
Here is how an alias can be defined:
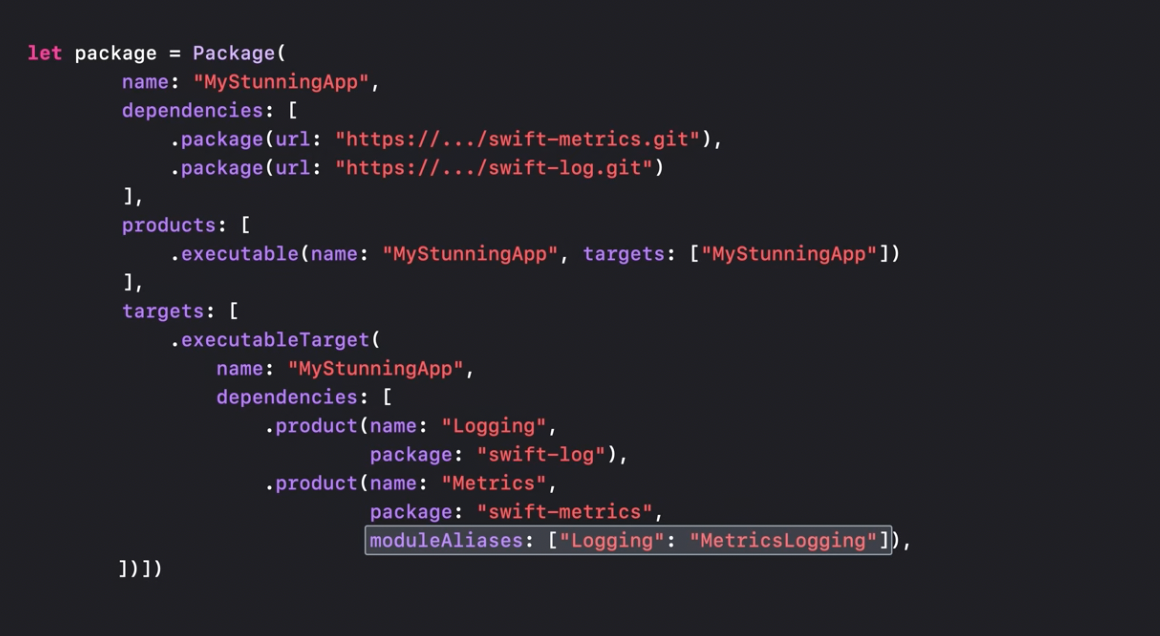
and then used:
Swift Compilation Performance
The "Swift Driver" which is a program that coordinates compilation was rewritten in Swift. It allowed to be integrated closer with Xcode's build system as a framework and unlocked new opportunities for parallel execution.
Recommended to watch:
- [[Demystify parallelization in Xcode builds - WWDC2022]]
Build time improvements
Reimplementation of Swift generics allowed to speed up the type checking of protocols and where clauses significantly. Sadly, but in Swift 5.6 time and memory complexity of protocols compilation used to be O(exp(N)). Now it's promised to be much better.
Run time improvements
Protocol conformance checking was optimized. Previously, protocols checking was performed every time the app launched, making it slower the more protocols involved. Now it's cached and makes apps launch up to 2x times faster on iOS16.
Recommended to watch:
- [[Improve app size and runtime performance - WWDC2022]]
Concurrency updates
Backport
Improvements in the concurrency model that was introduced last year were backported to
- MacOS 10.15
- iOS 13
- tvOS 13
- watchOS 6
To be able to run on older OS versions, the app bundles a copy of Swift5.5 concurrency runtime.
Improvements
- Data races avoidance
- Distributed actors
- Async algorithms
Data races avoidance
Similarly to the way how Swift cares about undefined behavior,

it would care about data races with a new actor model.

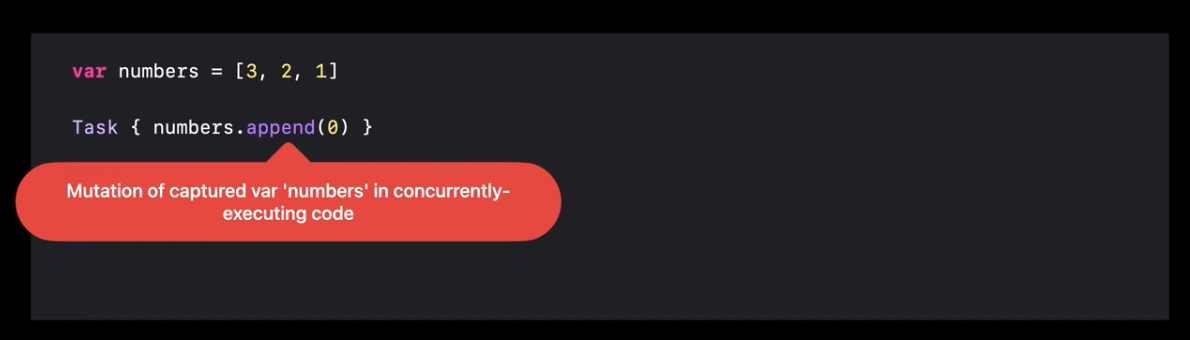
The actor isolates the data it works with.
Recommended to watch
- [[Eliminate data races using Swift Concurrency - WWDC2022]]
With the help of a robust concurrency model and opt-in safety checks to prevent potential data races, Swift is heading to its final goal which is to achieve complete thread safety in Swift 6
Distributed Actors
Distributed actors allow developers to encapsulate work that is done not just on different threads, but on different machines.
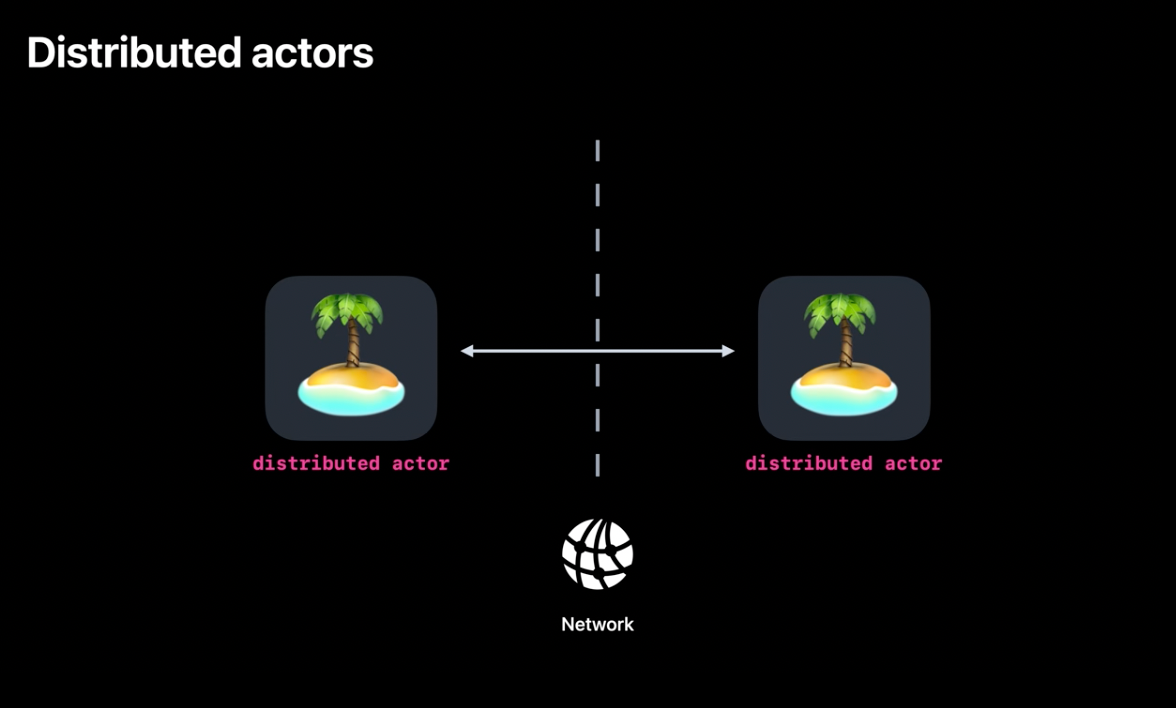
Distributed Actors package is open source and should make writing distributed systems in Swift much easier. Under the hood it uses SwiftNIO and it all must be nice for writing distributed backend solutions.
Recommended to watch
- [[Meet distributed actors in Swift - WWDC2022]]
Async algorithms package
An open-source package of async algorithms implementation was launched, supporting Apple platforms, Linux, and, for God's sake, Windows.
AsyncSequence is promised to be a very cool thing for dealing with time-based algorithms.
Recommended to watch
- [[Meet Swift Async Algorithms - WWDC2022]]
Concurrency Optimizations
Actors are deeply integrated with the OS scheduler allowing them to better prioritise work. Now There are new tools for measuring performance and visualizing concurrent tasks in Xcode instruments.

Recommended to watch
- [[Visualize and optimize Swift Concurrency - WWDC2022]]
Expressive Swift
Optionals unwrap sugar

Type inference improvements
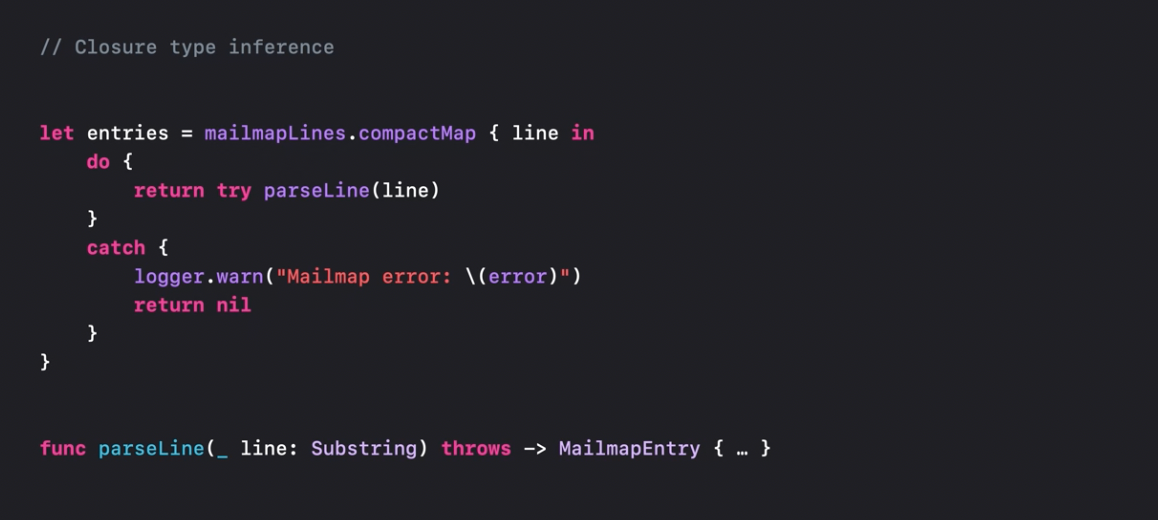
Swift interop with C changes
When dealing with C code, Swift now allows certain pointer conversions that we were not allowed before. It's done for sake of more seamless use of some C APIs.
In other cases, these conversions are still considered illegal in Swift:

New Regex Capabilities
Instead of writing regular expressions literally,
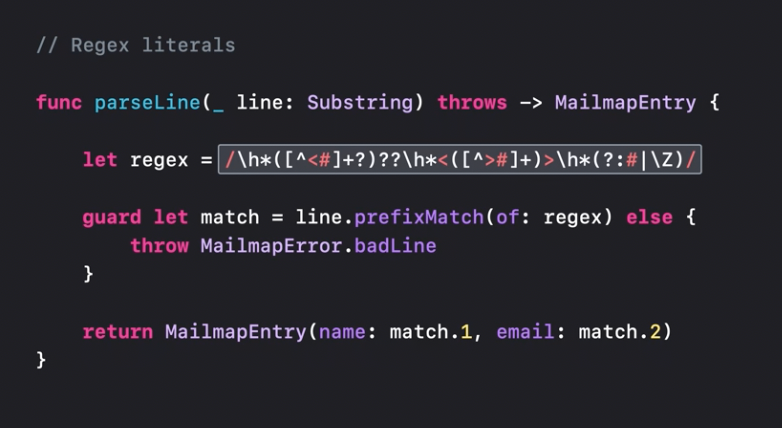
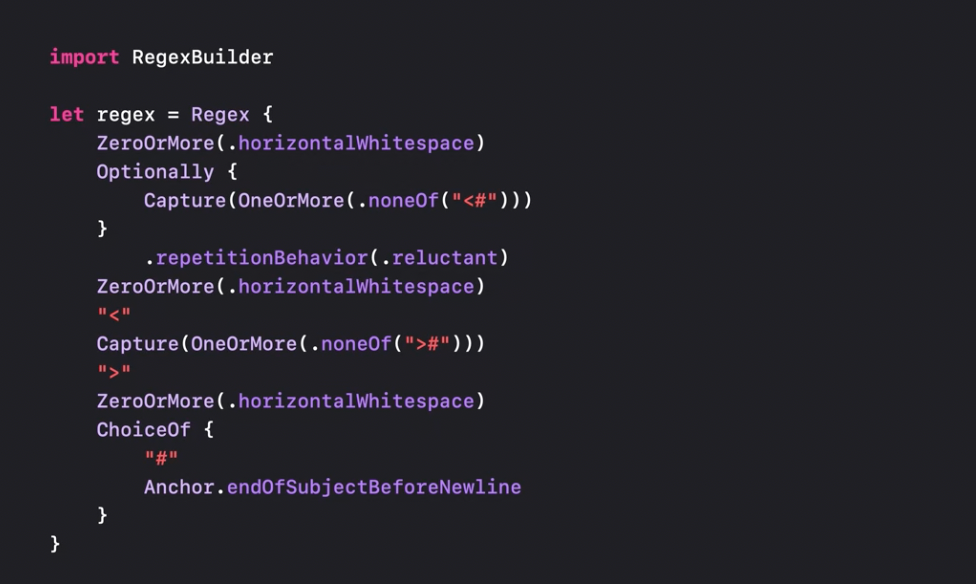
Now there is a possibility to use Regex Builder:
Regex can be turned into a reusable regex component, nested one into another, or used recursively.
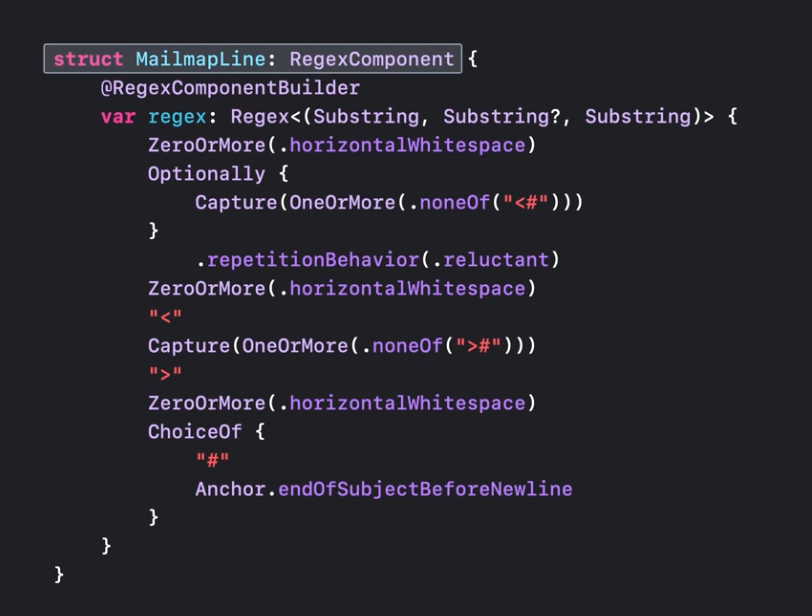
It also allows to include raw literal regex right inside the builder. And also allows converting the raw string captured data into a type
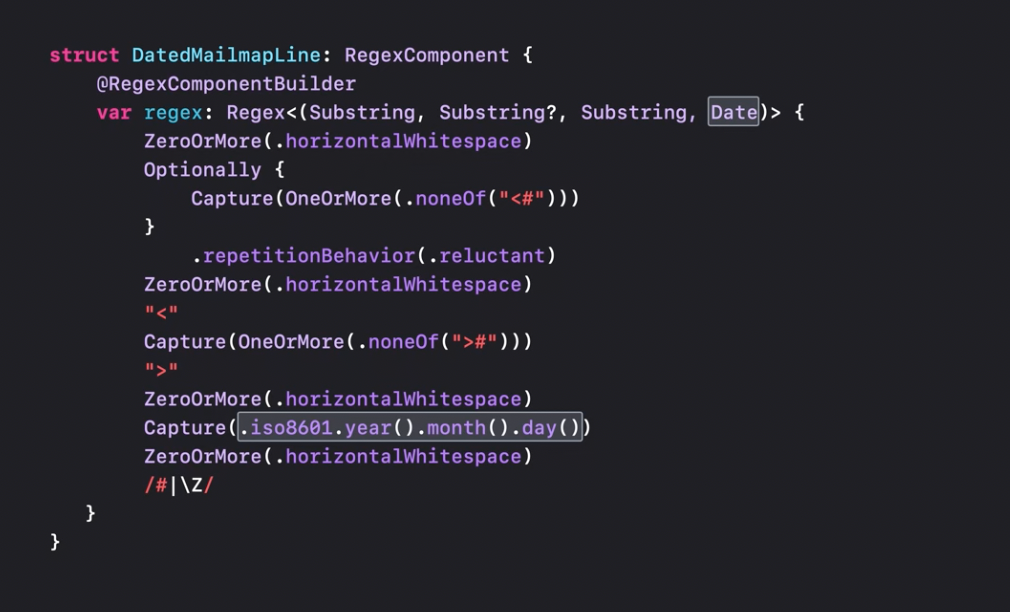
And use strongly typed captures:
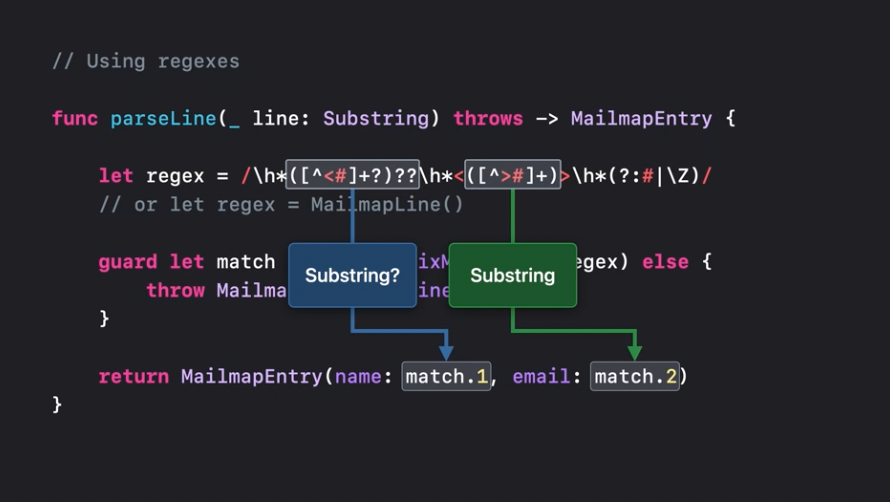
The new regex matching engine is written in Swift. Regex literal syntax is compatible with Unicode regex standard. Available in
- macOS 13,
- iOS16
- tvOS 16,
- watchOS 9
Recommended to watch:
- [[Meet Swift Regex - WWDC2022]]
- [[Swift Regex: Beyond the Basics - WWDC2022]]
Generic code clarity
Type erasure box
There used to be a great misunderstanding of Swift "protocols" as interfaces and protocols as generic type constraints which are somewhat of "Concepts" in C++. It was fairly easy to mess up those two things and end up suffering from poor design and having to write type-erasure wrappers and maintain them.
It looks like the generic type constraint protocol issues are finally fixed. In Swift 5.7 type erasure box is introduced.

Now we can use any keyword to mark a box that contains something that conforms to the specified protocol.

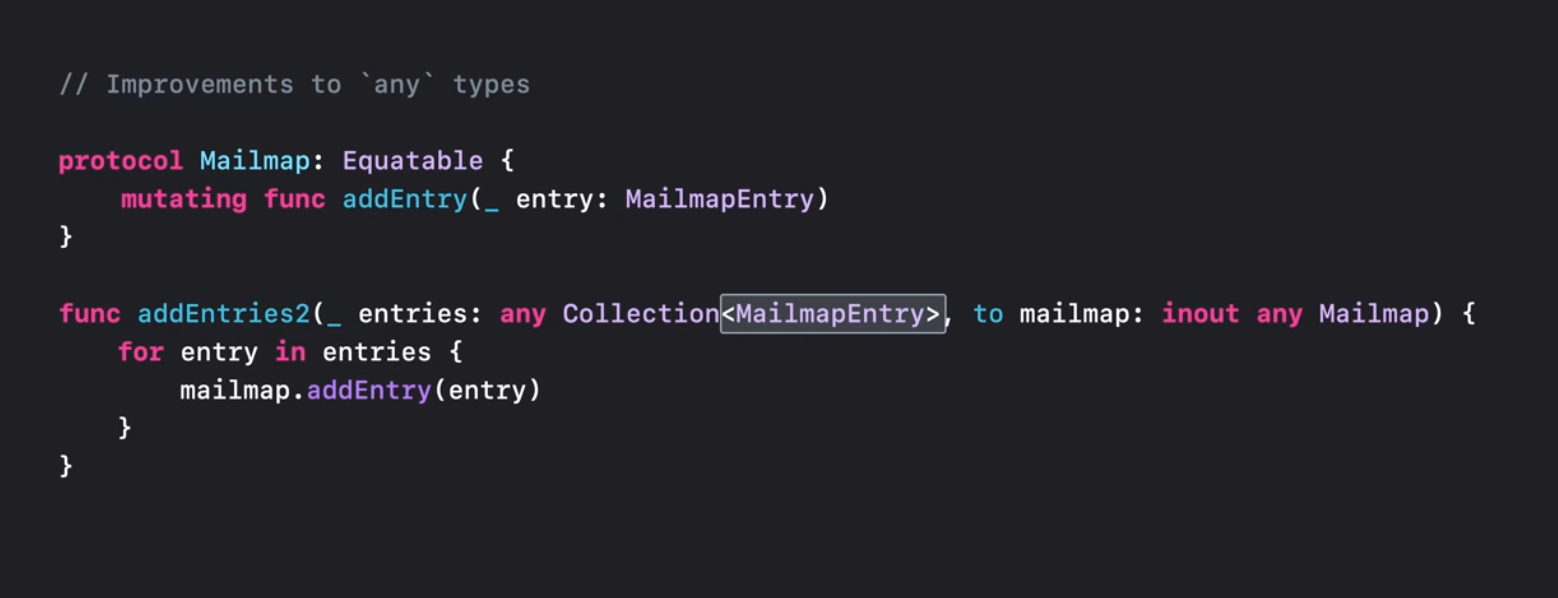
Primary protocol associate type
A protocol can have many associated types, that can be constrained and so on. The protocol's primary associated type is the one that the users of the protocol will later care most about.
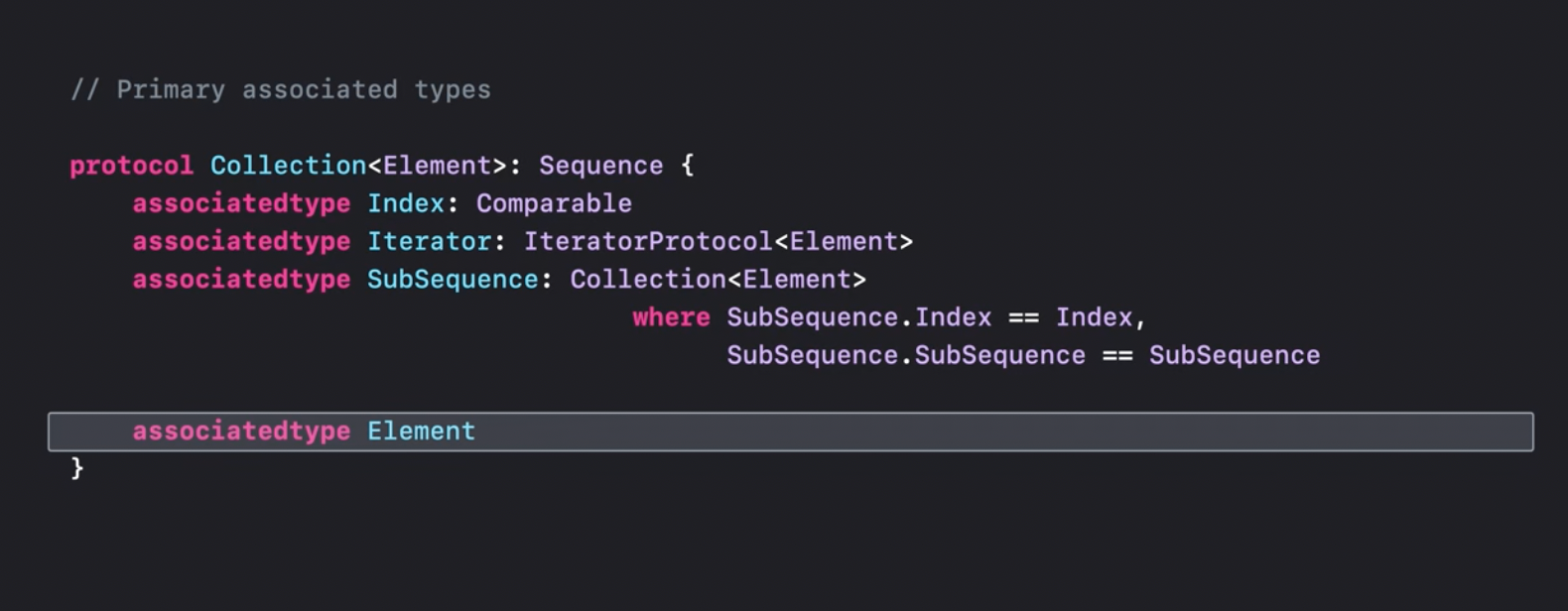
The protocol's primary associate type is a type that can be then erased in any box.
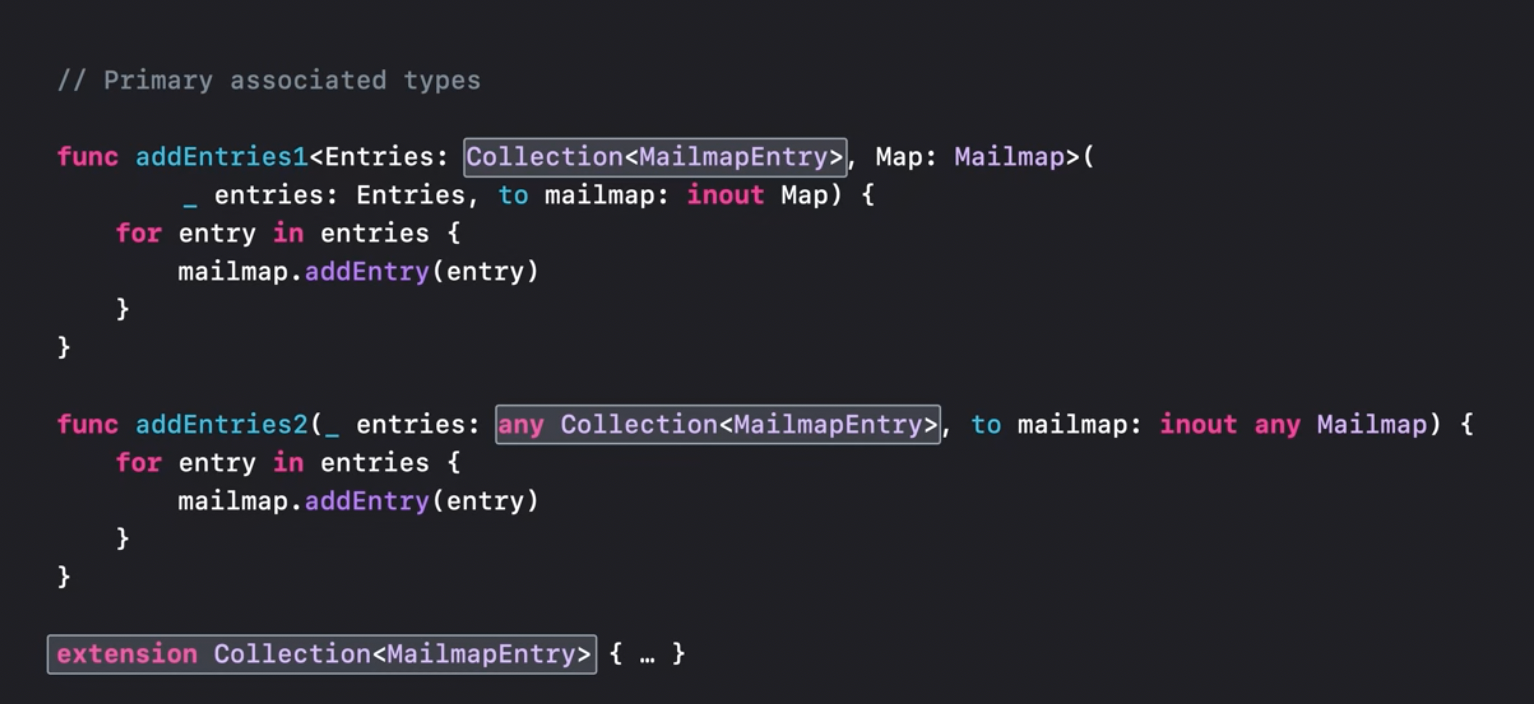
Finally, type erasure wrappers can be avoided by simply doing something like
typealias AnyAnimal = any Animal
However any box has still some limitations, like in Equatable where the comparison == requires parameters to be of the same type:

However, the generic version is still a preferred way to go at least because it's more efficient.
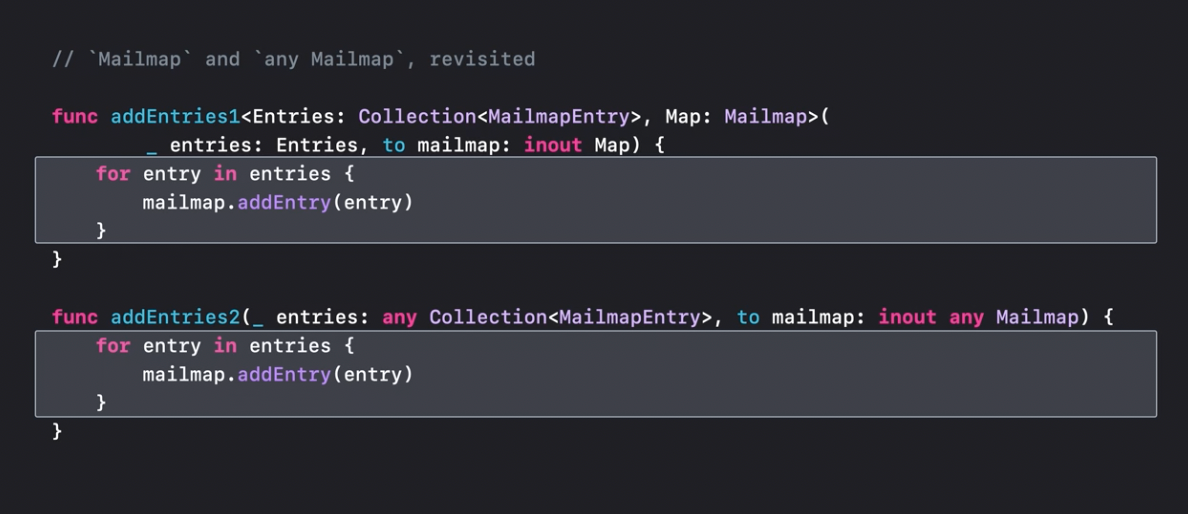
Syntax sugar for generics
To avoid writing extra code for generics, some keyword can now be used for generic type parameters.
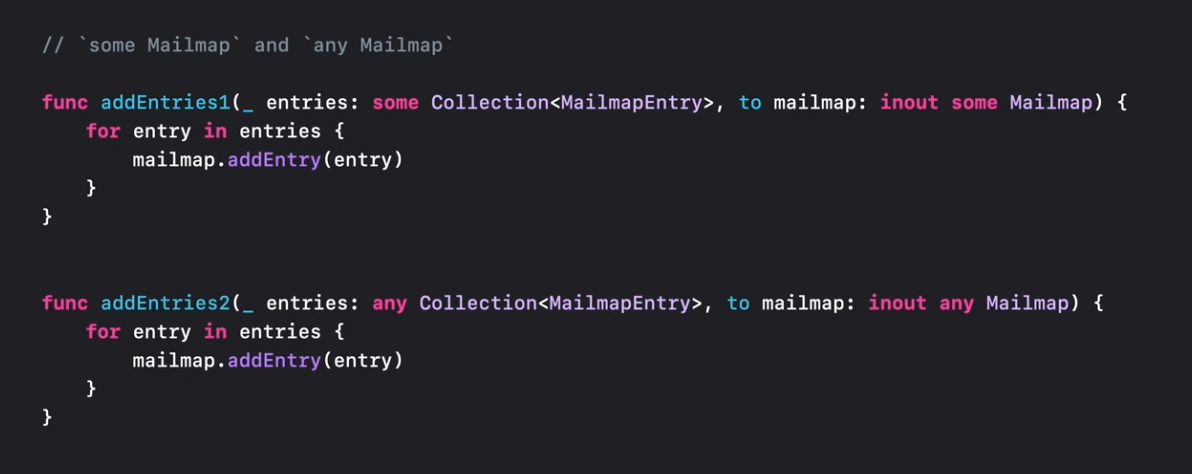
Recommended to watch:
- [[Embrace Swift generics - WWDC2022]]
- [[Design protocol interfaces in Swift - WWDC2022]]
Comments